The BNMA BN Repository
This repository is a resource for posting and downloading Bayesian network models for sharing with others and for providing supporting material for publications. Please respect authors' rights where noted.
Search
72 BNs found.
Marten Telomere Genetics for Age Determination
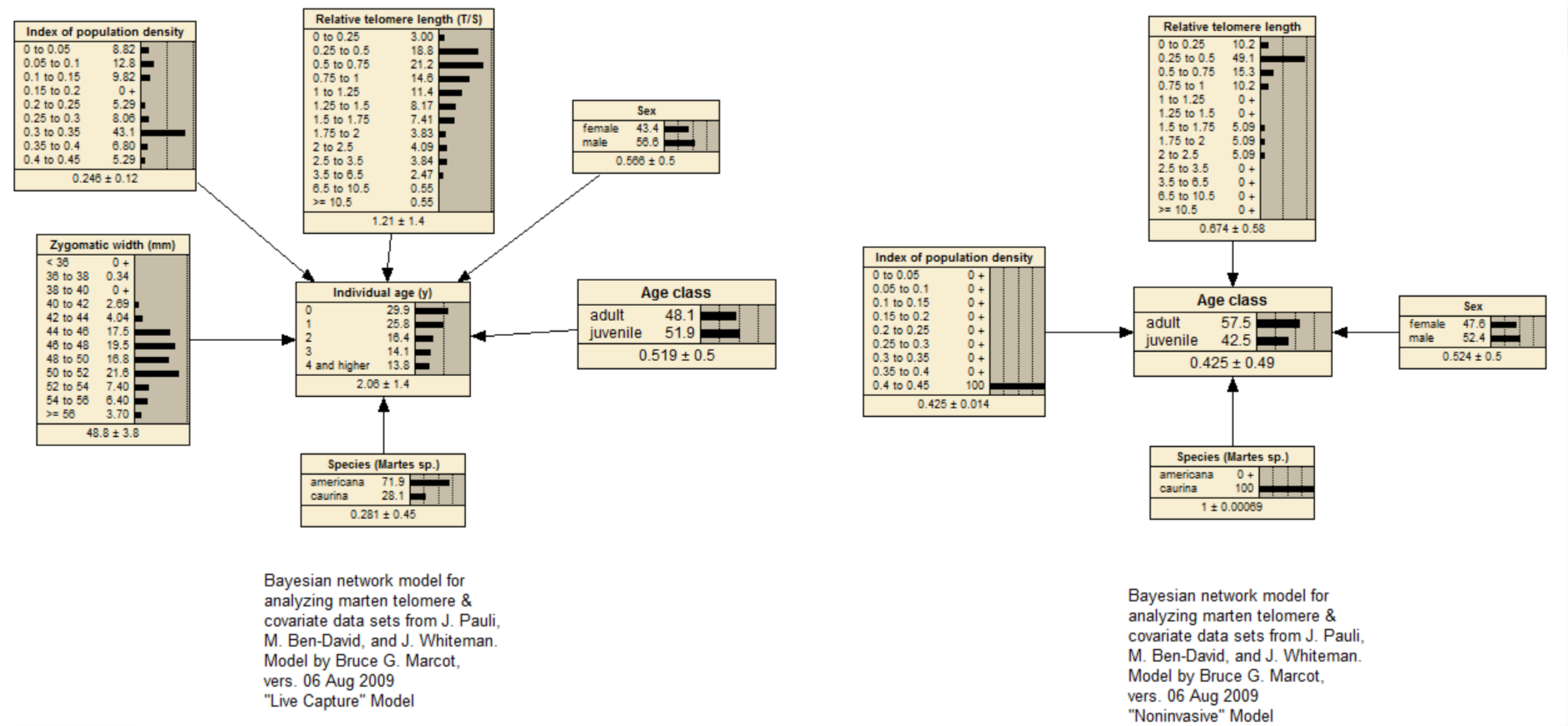
These models, trained from laboratory and field data, predict the age of individuals of two species of marten (Martes americana and M. caurina) in North America, from relative length of telomeres (fragmented ends of chromosomes that shorten over time) and other anatomical and environmental factors. It is the first time that age of an organism can be predicted from telomeres (and other factors) in a reliable manner. Two models are presented here: the "live capture" versions, for predicting age in years from captured (or museum specimen) martens; and the "noninvasive" version for predicting age class from non-invasive genetic samples where the actual animal does not need to be captured and handled. A case file for running the live capture model version can be found at <abnms.org...>.
Bull Trout Food Web
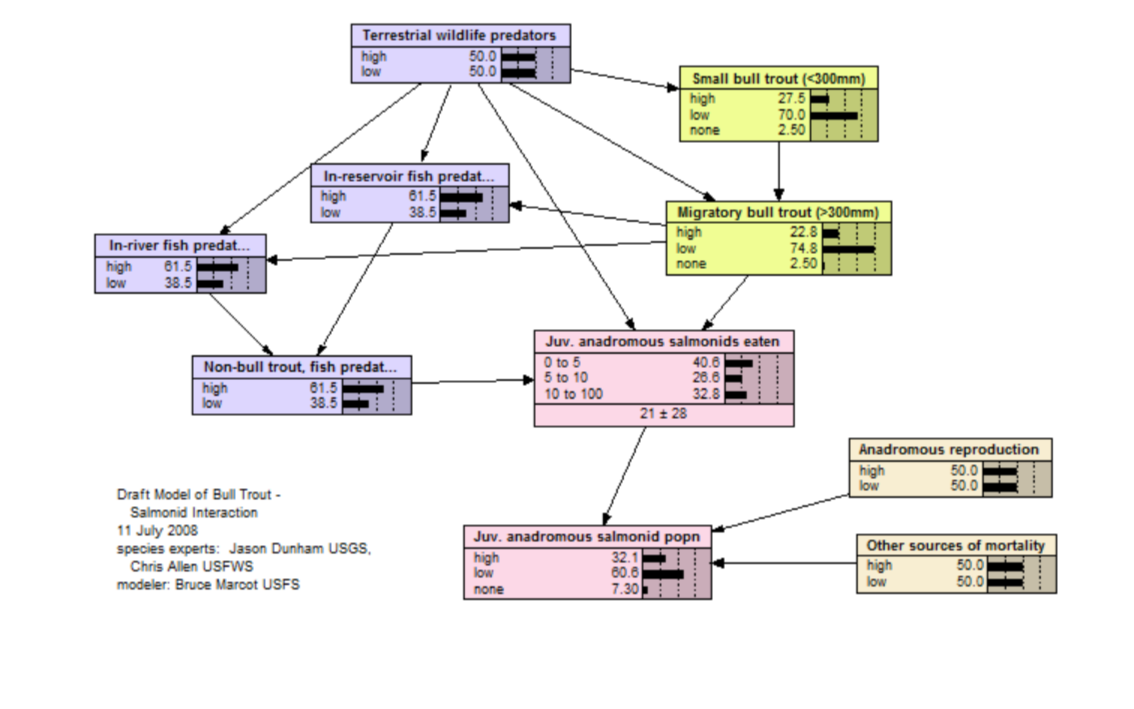
This model illustrates potential food web and species interaction dynamics related to interactions between bull trout (Salvelinus confluentus) and anadromous salmonid fish existing in the same river system. (Explanation of nodes: small bull trout = at least juveniles and possibly resident adults; terrestrial wildlife predators = some amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals; juvenile [juv.] anadromous salmonids eaten = average annual percentage of total juvenile anadromous salmonids that are consumed by fish and other predators; juvenile anadromous salmonids = parr to smolt stages, although some bull trout predation on eggs also occurs; popn = population; anadromous reproduction = number of offspring [embryos] produced by spawning adult salmonids; other sources of mortality = poor water quality, passage through reservoirs and past dams, natural disturbances, etc.).
Pacific Walrus
We developed a Bayesian network model to integrate potential effects of changing environmental conditions and anthropogenic stressors on the future status of the Pacific walrus population in the Chukchi and Bering Seas, at four periods through the twenty-first century. The model framework allowed for inclusion of various sources and levels of knowledge, and representation of structural and parameter uncertainties. Walrus outcome probabilities through the century reflected a clear trend of worsening conditions for the subspecies.
Polar Bear Stressor Model, Phase I (2007-08)
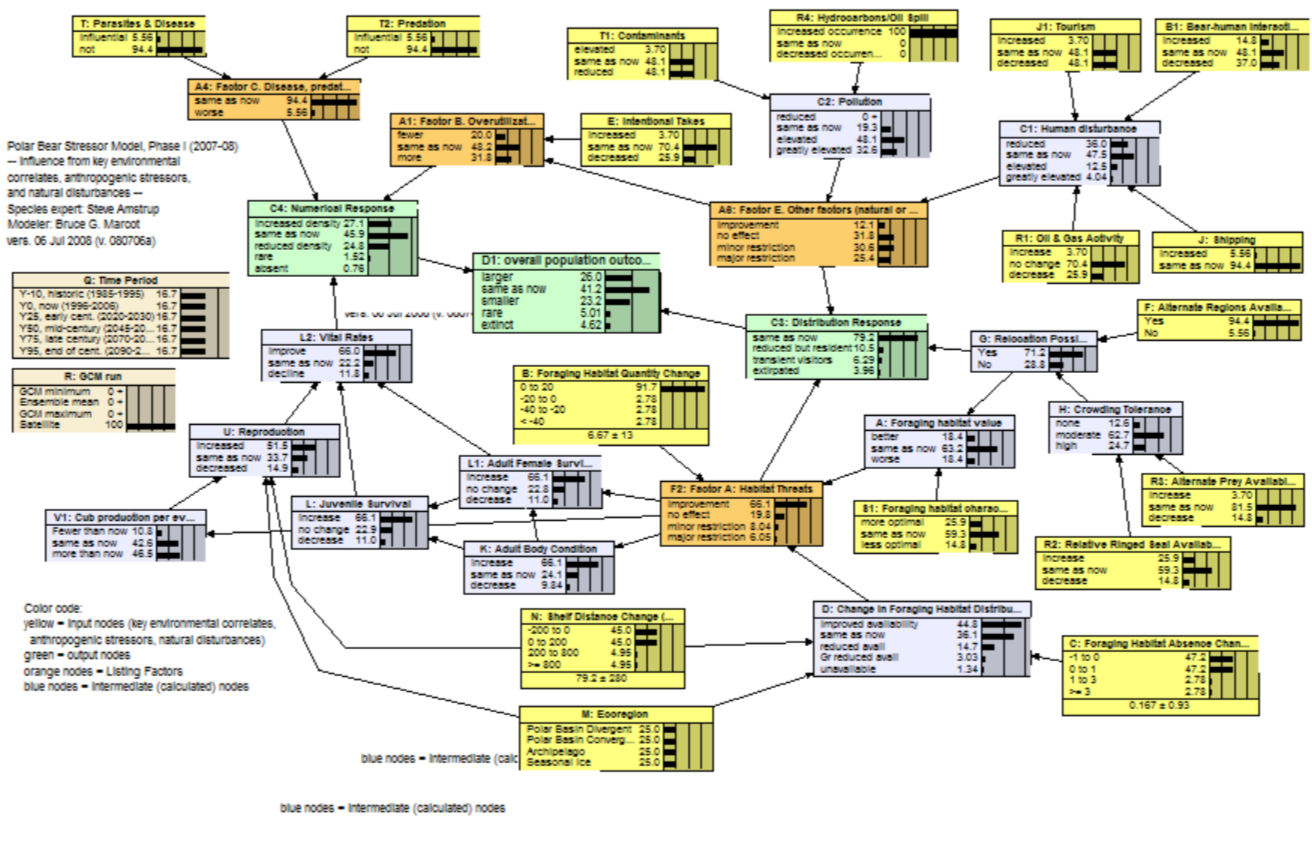
In 2007-08, to inform the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service decision, whether or not to list polar bears as threatened under the Endangered Species Act (ESA), we projected the status of the world’s polar bears (Ursus maritimus) for decades centered on future years 2025, 2050, 2075, and 2095. We defined four ecoregions based on current and projected sea ice conditions: seasonal ice, Canadian Archipelago, polar basin divergent, and polar basin convergent ecoregions. We incorporated general circulation model projections of future sea ice into a Bayesian network (BN) model structured around the factors considered in ESA decisions. This first-generation (Phase I) BN model combined empirical data, interpretations of data, and professional judgments of one polar bear expert into a probabilistic framework that identifies causal links between environmental stressors and polar bear responses. The BN model projected extirpation of polar bears from the seasonal ice and polar basin divergent ecoregions, where ≈2/3 of the world’s polar bears currently occur, by mid century. Decline in ice habitat was the overriding factor driving the model outcomes.
The Polar Bear Stressor Model, Phase II (2016) can be found here: <abnms.org...>
Recreation Effects on Brown Bears
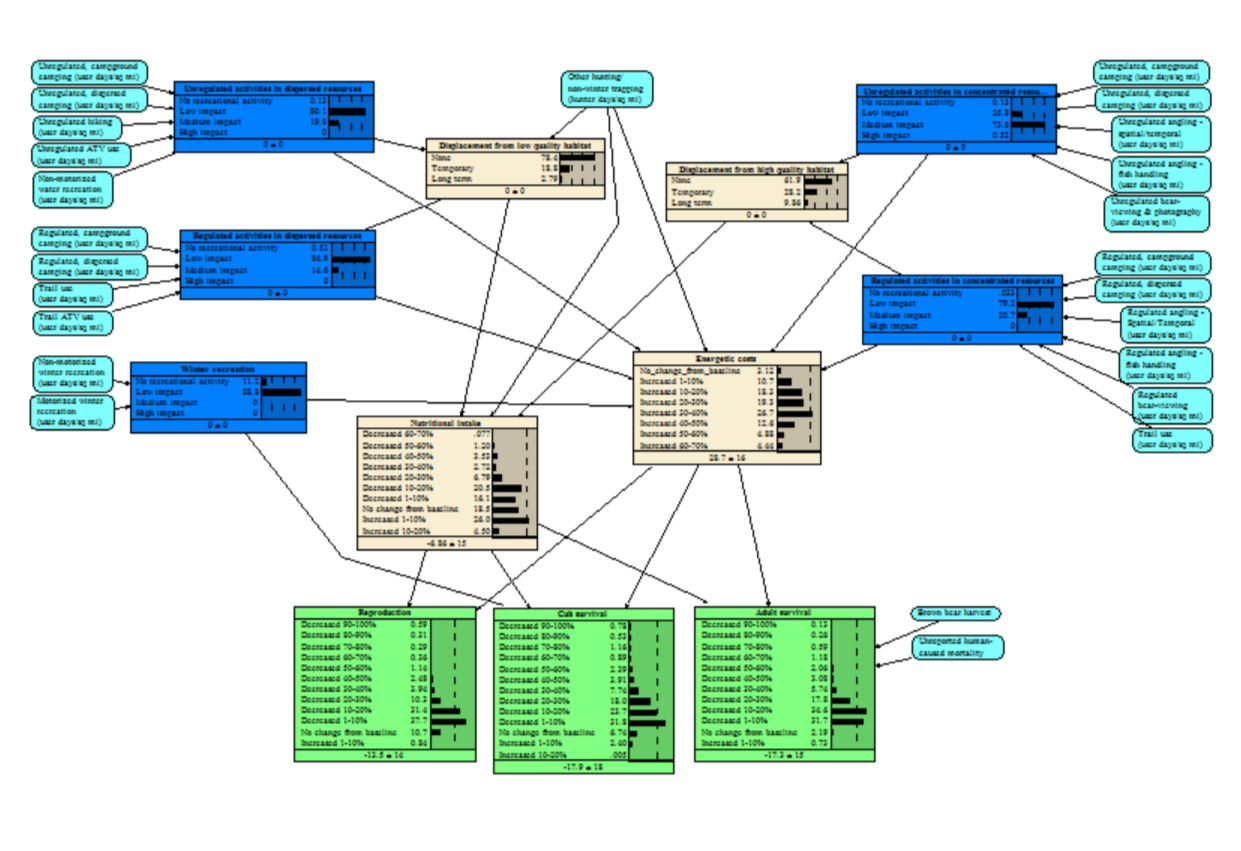
We integrated results from empirical studies with expert opinion to better understand the potential population-level effects of recreational activities on brown bears. We conducted a literature review and Delphi survey of brown bear experts to better understand the frequencies and types of recreations occurring in bear habitats and their potential effects, and to identify management solutions and research needs. We then developed a Bayesian network model that allows managers to estimate the potential effects of recreational management decisions in bear habitats.
BPP: The Bayesian Poker Player
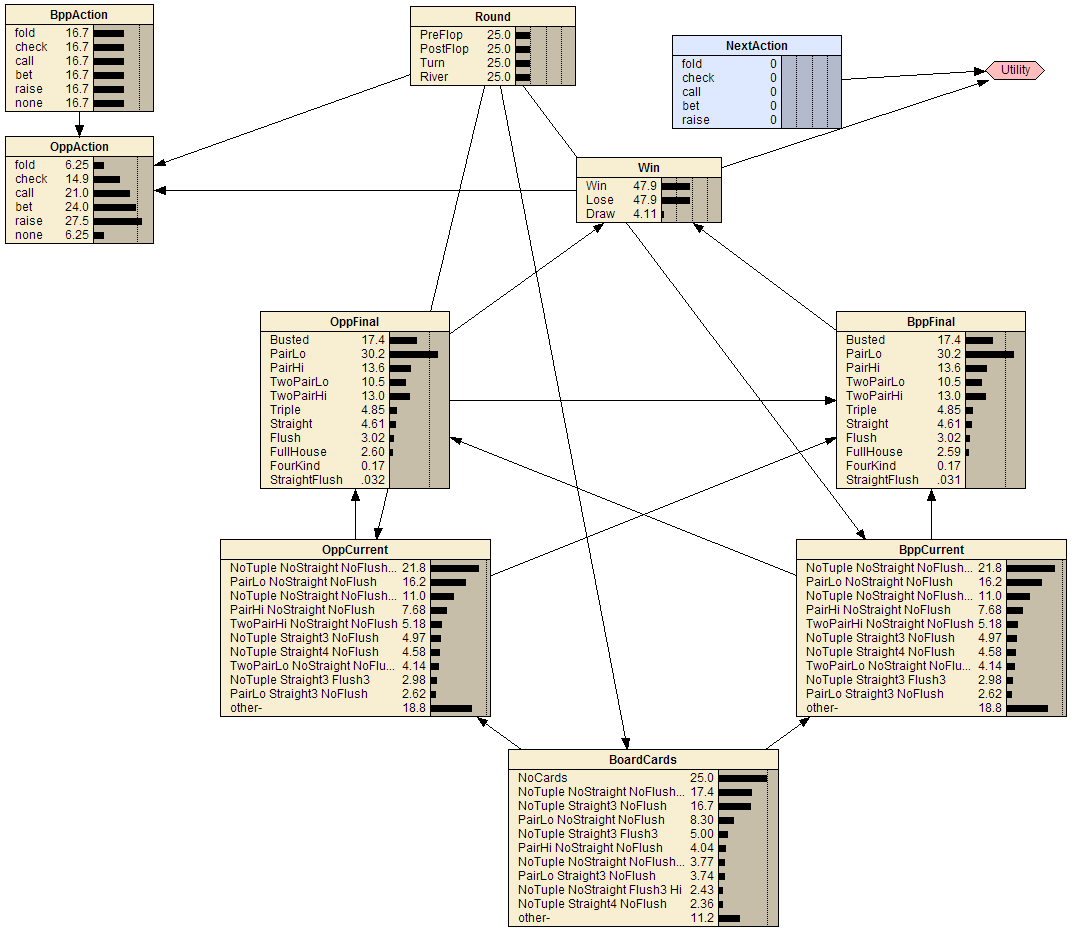
The Bayesian Poker Player (BPP) began life as an honours project at Monash in 1993. Since then several honours students have worked on various aspects of the project and some of the work has been written up as research publications. BPP was originally developed to play 5-card stud poker, using Bayesian network technology. In 2006, BPP was converted to play Texas Hold'em Poker, the main online form of poker, and re-written in Python. We have developed a simple GUI interface that allows people to play against BPP online, which is hosted here: <bayesian-intelligence.com...>. This is an ongoing project in which there are still many options for making BPP a better poker player including improving its bluffing strategies and its opponent modelling.
Habitat Suitability
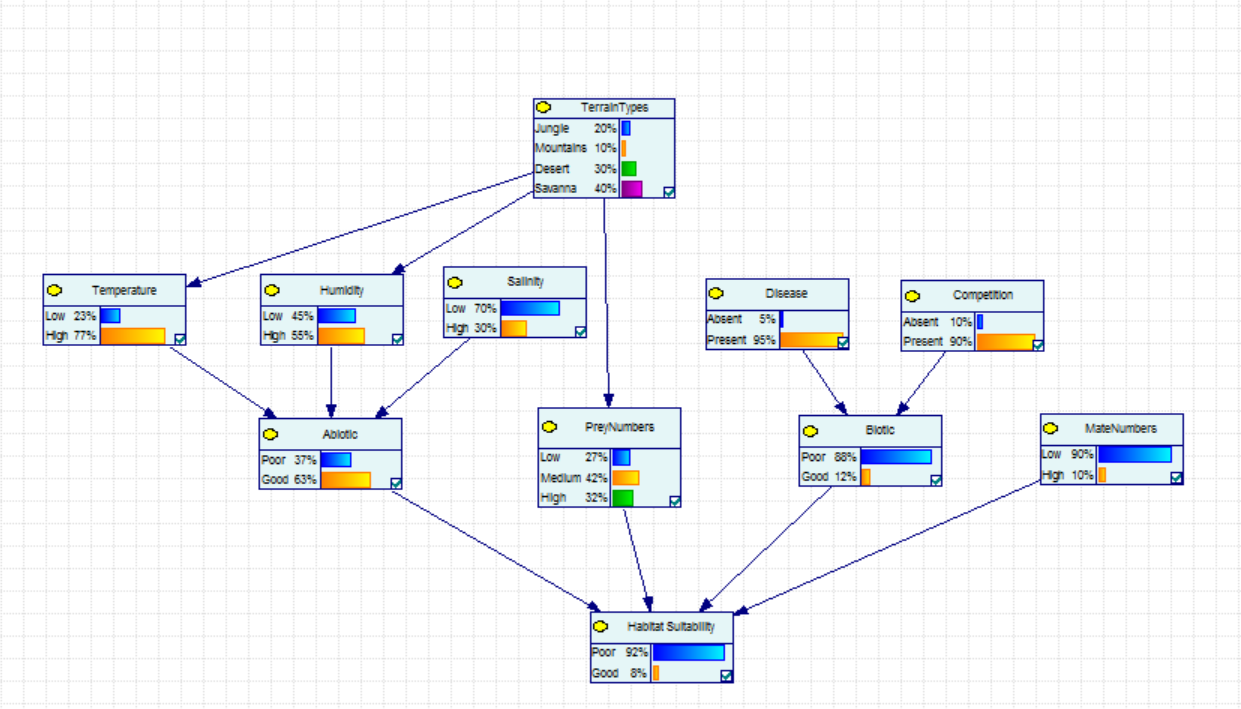
The habitat suitability problem is one where a close to extinct species has to be moved to another country/continent to determine if the species can successfully survive.
In this example, the Sumatran tiger (close to extinction) is to be relocated to central Africa where the habitat is to be assessed for its suitability.
Rail Maintenance Modelling
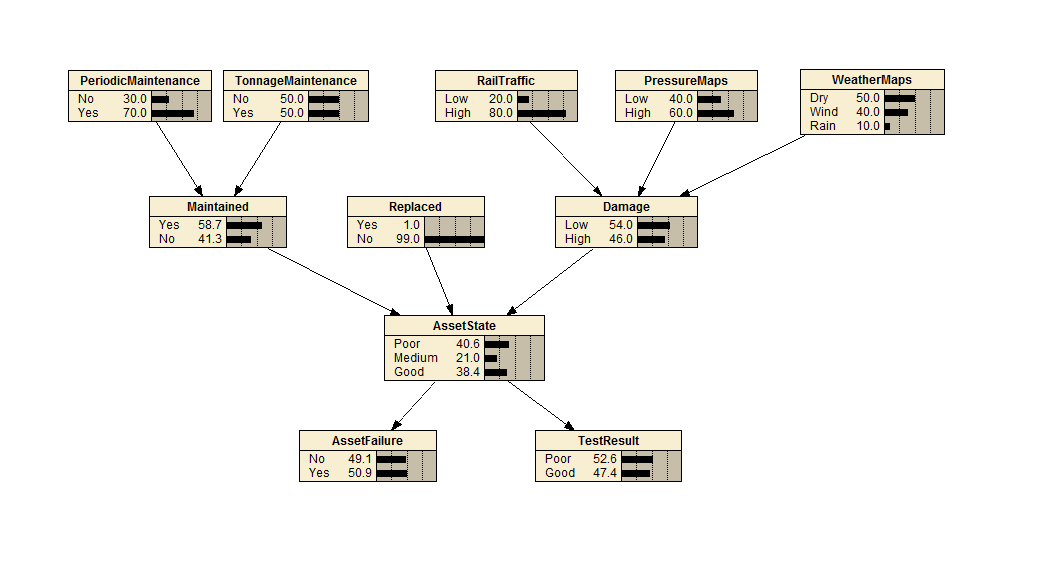
Rail maintenance modelling is the problem of determining the failure of an asset (e.g. tracks) given various factors. In this example, the factors chosen are weather, maintenance history (tonnage and periodic) and rail traffic. The temporal scale is assumed to be yearly.
There are various parts of the model that could be expanded. For example, maintenance types could be included or individual asset types could be modelled.
Oil & Gas Drilling
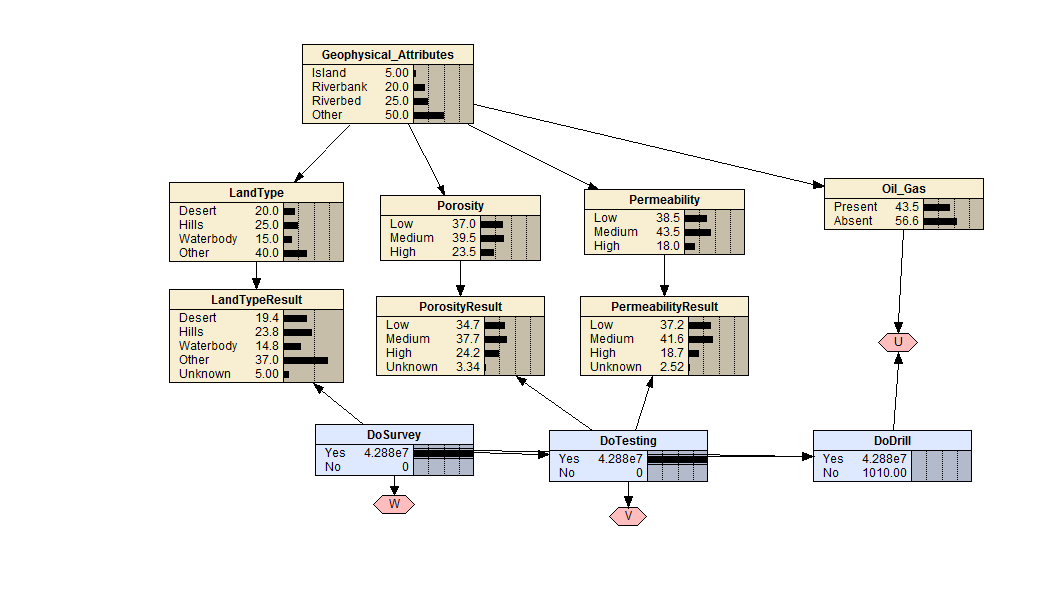
The following is a simplified model of a typical Oil & Gas mining problem. Firstly, the exploration process aims to identify regions with high probability of success (survey). These regions can be inland or off-shore and typically, after being identified, are expected to consist of one or more sweet-spots. Secondly, an initial drill (testing) at the location in question is carried out to determine if sufficient levels of hydrocarbons exist to allow extraction to be a long term option. This is followed by further drills (drill) eventually leading to production.
The costs associated with drilling are variable depending on drilling conditions and variability of the underlying soil layers and are usually very high. Additionally, drilling can be unsuccessful due to blow-outs, issues with equipment (insufficient, failure) and other accidents. These aspects are accounted for via costs and are built into the utility nodes.
Koalas
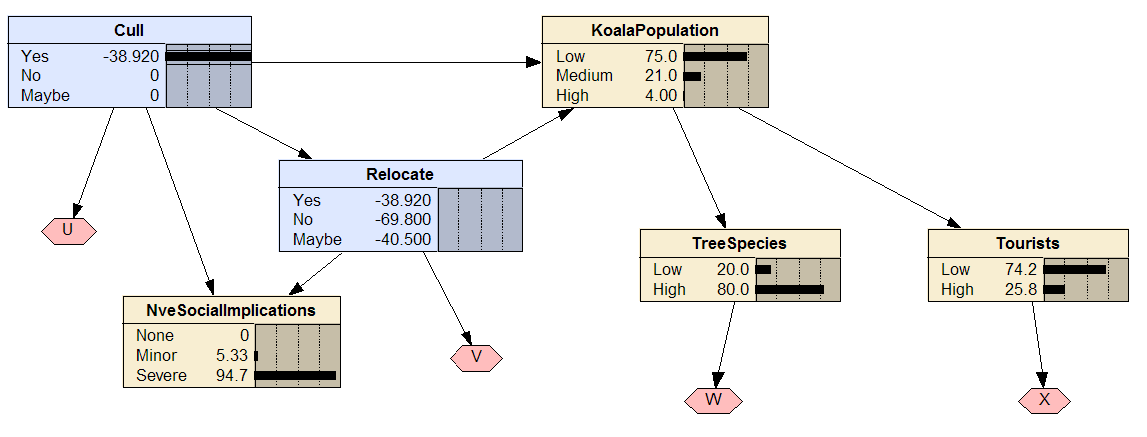
Fraser Island in Queensland did not traditionally house Koala populations. However, since they were brought to the island they have provided benefits and have also caused problems. On a positive note, they are an attraction for tourists providing the island authorities with resources for maintenance. Conversely, they tend to disrupt the flora, even wiping out species of trees if they are not monitored. Thus, in order to maintain healthy populations without damage to the environment, the authorities can decide to cull a number of Koalas (inexpensive) or relocate to the mainland (expensive) where they are already well adapted. Additionally, animal welfare groups do not take kindly to culling.
Note: this is a fictitious example.
Revolver

This is a modified version of Russian roulette. We are given a gun with six chambers and two bullets in two consecutive chambers. I first take a shot and pass the gun to you. You must take the second shot, but you can choose to spin the chamber first, or leave it untouched. What do you choose to do?
Monty Hall Decision Problem
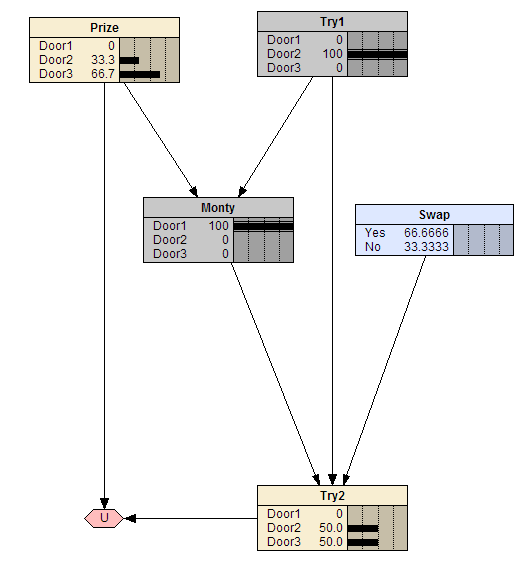
The Monty Hall problem (see <en.wikipedia.org...>) is a simple counter-intuitive puzzle. There are three doors, two of which have goats behind them and third door, a car. First, you pick a door. Monty then chooses a door with a goat behind it. Now it is up to you: Stay with your door or swap to the other unopened door?
Socioeconomic Status DBN
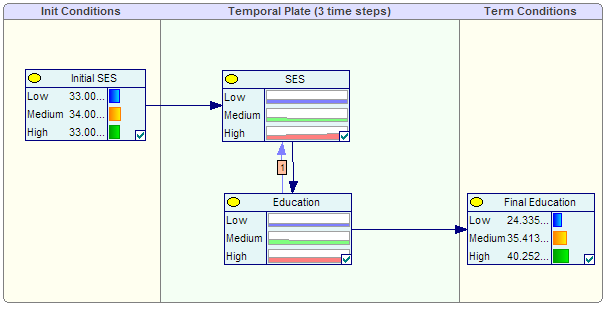
This BN is an example of dynamic Bayesian network which includes feedback loops. The feedback loop represents the commonly accepted feedback relationship between socioeconomic status and education.
Waterhole Fence

An assessment of the expected value of putting in a fence to promote plant survival, in the face of factors that affect the durability of the fence.
Go Surfing?
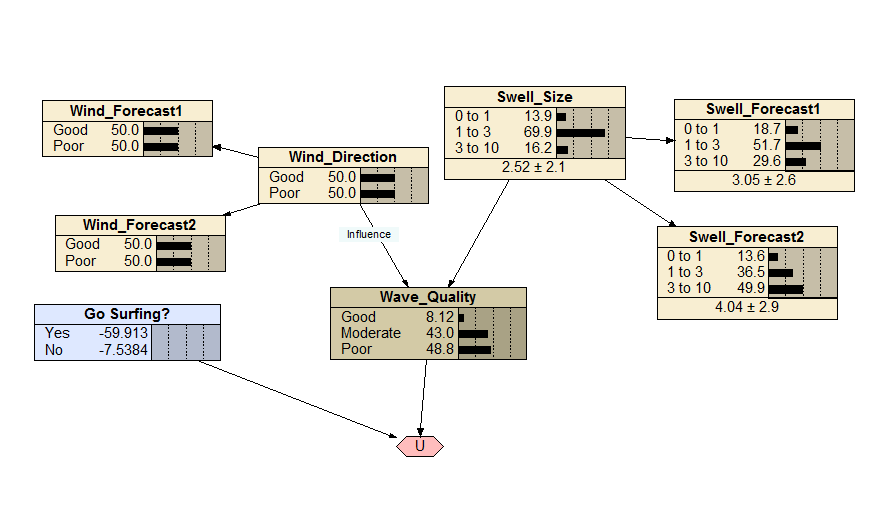
An example decision network for the dilemma of whether or not one should go surfing. The expected value of heading into the surf (or remaining put) is dependent on the wave quality, which is in turn dependent on wind direction and swell size. Both the wind direction and the swell size can be (imperfectly) forecast, and examples of handling these imperfect forecasts are included in the network.
Steroid Use Check
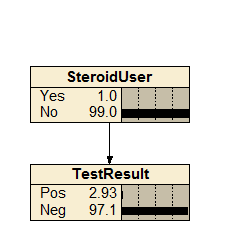
An extremely simple 2-node example demonstrating how true positive/false positive cases can be handled, in this case as applied to a steroid use test.
Popperian Language Patterns
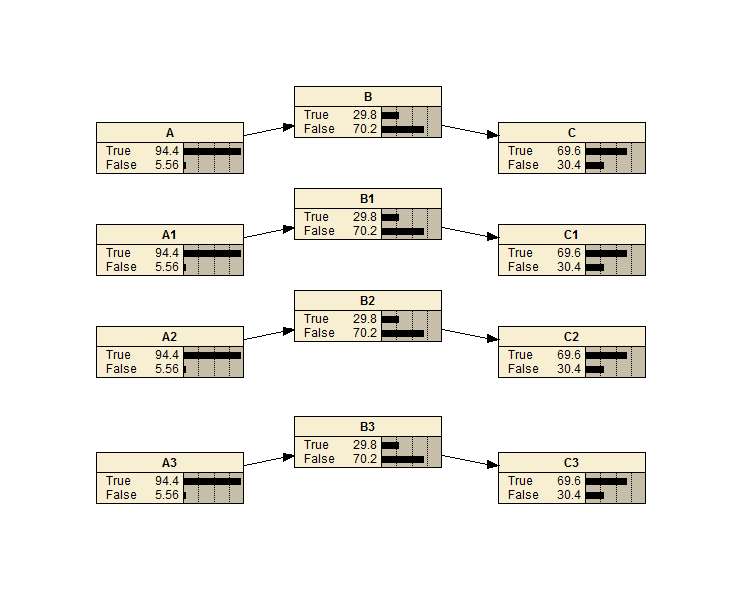
An example of causal discovery where it can falsify the one causal pattern or the other in the Popperian language through its patterns. The BN learns three chains partially and the design can then be scaled up.
Motion
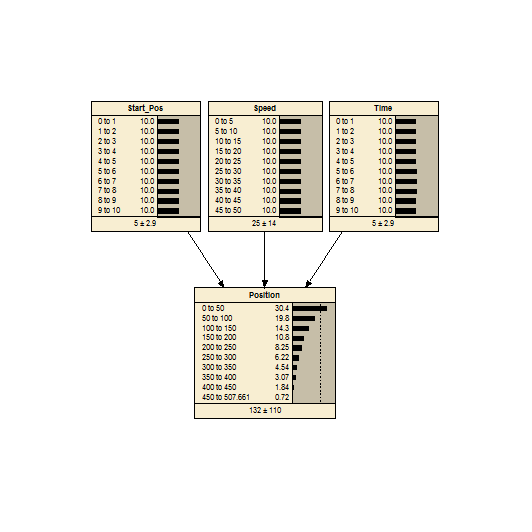
An example of using CPT equations in Netica. The main equation is very simple and updates the final position given the initial position, speed and time.
Amniocentesis Test

A decision network which decides if an Amniocentesis test provides a probability of a positive or negative result given the mother's age. It also provides the probability of a miscarriage should the test not be carried out appropriately. Amniocentesis is a test that can be done on pregnant women to test for certain foetal abnormalities, such as Down’s Syndrome.
Native Fish V1
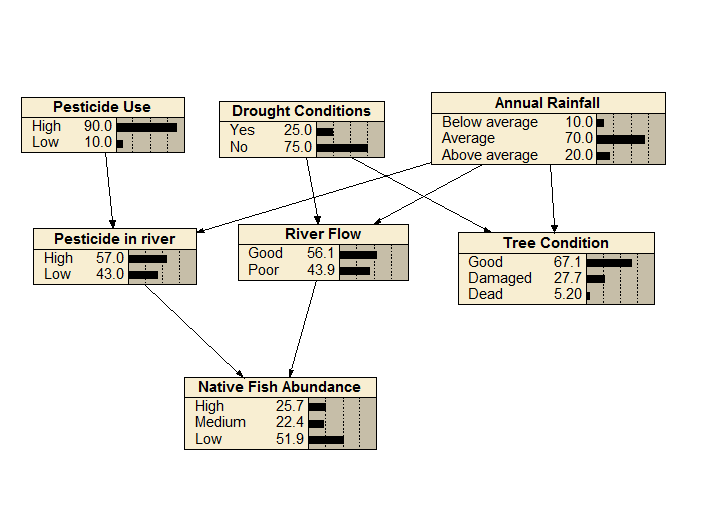
This BN calculates the probability of native fish abundance given pesticide in use and in river, drought conditions, river flow, annual rainfall and tree conditions.
 Bayesian Intelligence
Bayesian Intelligence